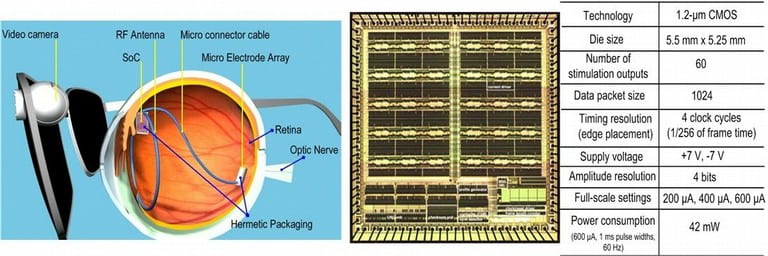
We continue our pioneering work on Retinal Prosthesis to restore vision in blind patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) and Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) through developing the next generation retinal implants. The goal of these implants is more than 1000 pixels that would enable facial recognition and independent mobility. The project focuses on delivering power and data to the retinal implant inside the eye and the implant microstimulator electronics which delivers the current pulses to stimulate the retinal layer to elicit visual perception. Since the use of invasive means such as tethering wires results in discomfort and potential infection, a completely wireless approach is used to transfer both power and data. Since the coupling between the external unit consisting of the power transmitter and the power receiver can vary due to the patient’s movements, a closed loop approach is used which varies the transmitted power dynamically to automatically compensate for such movements. We are collaborating with the medical team in University of Southern California and several national laboratories for this project.

Selected Publications
- “Retinal Prosthesis,” J. D. Weiland, W. Liu, and M. S. Humayun, Volume: 7, Pages: 361 – 401, Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, August 2005.
- “A Core Component for Neuro Stimulus with Telemetry Unit,” W. Liu, M. Humayun, K. Vichienchom, M. Clements, S. DeMarco, E. McGucken, C. Hughes, E. de Juan, J. Weiland, R. Greenberg, Volume: 35, Pages: 1487-1497, IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, October 2000.
Collaborators
- University of Southern California
- California Institute of Technology
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- Sandia National Laboratory
- Argonne National Laboratory